Libra (constellation)
| Constellation | |
List of stars in Libra |
|
| Abbreviation | Lib |
|---|---|
| Genitive | Librae |
| Pronunciation | /ˈliːbrə/, genitive /ˈlaɪbriː/ |
| Symbolism | the Scale |
| Right ascension | 15 h |
| Declination | −15° |
| Quadrant | SQ3 |
| Area | 538 sq. deg. (29th) |
| Main stars | 4, 6 |
| Bayer/Flamsteed stars |
46 |
| Stars with planets | 3 |
| Stars brighter than 3.00m | 2 |
| Stars within 10.00 pc (32.62 ly) | 5 |
| Brightest star | Zubeneschamali (β Lib) (2.61m) |
| Nearest star | Gliese 570 (19.20 ly, 5.89 pc) |
| Messier objects | 0 |
| Meteor showers | May Librids |
| Bordering constellations |
Serpens Caput Virgo Hydra Centaurus (corner) Lupus Scorpius Ophiuchus |
| Visible at latitudes between +65° and −90°. Best visible at 21:00 (9 p.m.) during the month of June. |
|
Libra is a constellation of the zodiac. Its name is Latin for weighing scales, and its symbol is ![]() (Unicode ♎). It is fairly faint, with no first magnitude stars, and lies between Virgo to the west and Scorpius to the east.
(Unicode ♎). It is fairly faint, with no first magnitude stars, and lies between Virgo to the west and Scorpius to the east.
Contents |
Notable features

The brightest stars in Libra form a quadrangle:
- α Librae, Zubenelgenubi ("southern claw"), a visual binary;
- β Librae, Zubeneschamali ("northern claw");
- γ Librae, Zubenelakrab ("scorpion's claw");
- σ Librae, Brachium an eclipsing variable.
σ Librae was formerly known as γ Scorpii despite being well inside the boundaries of Libra. It was not redesignated as σ Librae until 1851 (by Benjamin A. Gould).
Planetary system
Libra is home to the star Gliese 581, which has a planetary system consisting of at least 4 planets, including, Gliese 581 c, the first Earth-like extrasolar planet to be found within its parent star's habitable zone, Gliese 581 d, discovered in 2007 to be another Earth-like planet, and Gliese 581 e, the smallest mass exoplanet orbiting a normal star,[1] both of which are of significance for establishing the likelihood of life outside of the Solar System.[2]
History and Mythology
In earlier times, Libra was represented not by a balance, but as the claws of a scorpion. The reason is a confused translation of the words zubānā in Arabic and zibanitu in Akkadian, which mean both 'weighing scale' and 'scorpion'. In ancient Mesopotamia, a weighing scale was often the arm and the pans without a stand, and was hung up by a string tied to the midpoint of the arm, resulting in a close resemblance to a scorpion hung up by the end of its tail with its arms stretched out.
The double meaning of zibanitu resulted in the constellation being called Chelae Scorpionis (the scorpion's claws), and it originally formed part of the claws of the Scorpius. The modern Libra is the youngest of the Zodiac signs and the only one not to represent a living creature. In Greek mythology, Libra is considered to depict the scales held by Astraea (identified as Virgo), the goddess of justice.
Astrology
As of 2002[update], the Sun appears in the constellation Libra from October 31 to November 22. In tropical astrology, the Sun is considered to be in the sign Libra from September 23 to October 22, and in sidereal astrology, from October 16 to November 15. The symbol for Libra is the Scales, making it the only zodiac sign of which the symbol is not a living creature.
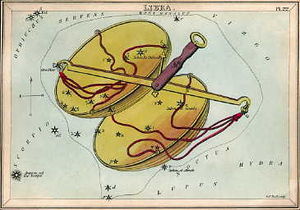
Visualizations
Traditionally, α and β Librae are considered to represent the scales' balance beam, and γ and σ are the weighing pans.
H.A. Rey has suggested a way to connect the stars more fully to graphically show a balance. The star beta Librae, of third magnitude, represents the top of the balance. The stars gamma Librae and alpha Librae represent the balance beam: alpha Librae being of third magnitude as well. The stars upsilon Librae and tau Librae represent the left plate of the balance, whereas the star sigma Librae represents the right plate of the balance. All three of these stars are of the third magnitude.
Citations
References
- H. A. Rey, The Stars — A New Way To See Them. Enlarged World-Wide Edition. Houghton Mifflin, Boston, 1997. ISBN 0-395-24830-2.
- Ian Ridpath and Wil Tirion (2007). Stars and Planets Guide, Collins, London. ISBN 978-0007251209. Princeton University Press, Princeton. ISBN 978-0691135564.
External links
|
|||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Astronomy | Constellations of the Zodiac |
|---|
| Pisces ★ Aries ★ Taurus ★ Gemini ★ Cancer ★ Leo ★ Virgo ★ Libra ★ Scorpius ★ Ophiuchus ★ Sagittarius ★ Capricornus ★ Aquarius |